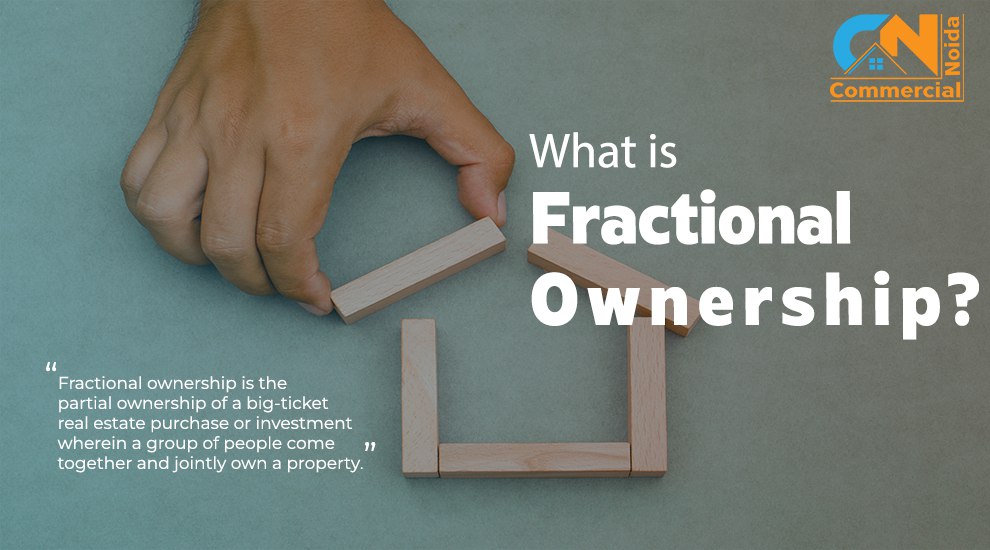
Distinction between Testamentary and Intestate Succession?

Difference Between Testamentary & Intestate Succession – A Legal Overview
When a person dies, their property and assets are transferred to their family members or legal heirs. This process is called succession. In India, succession plays an important role in determining who gets what after the death of a person.
This blog explains the types of successions in India. Whether you are a property buyer, investor, or someone looking for legal knowledge, this article will help you understand the topic easily.
What is Succession?
Succession means the legal process of passing the property of a deceased person to their heirs. The person who dies is called the deceased. The people who receive the property are called heirs or successors.
Succession can happen in two ways:
1. When the person has made a will before dying.
2. When the person has not made any will.
Based on this, succession in India is divided into two main types:
• Testamentary Succession
• Intestate Succession
Now, let us understand these types in detail.
Testamentary Succession
Testamentary succession takes place when a person dies after writing a will. A will is a legal document in which a person mentions who will receive their property after death. The person who writes the will is called a testator. The people who receive the property through the will are called beneficiaries.
In testamentary succession, the property is divided exactly as mentioned in the will. It gives freedom to the person to distribute property according to their wishes, even if it is different from the legal rules.
For a will to be valid, it must be:
• Written clearly
• Signed by the testator
• Signed by at least two witnesses
If there is any confusion or dispute, the court can check the will and give a final decision. This process is called probate.
Intestate Succession
When a person dies without writing a will, it is called intestate death. In such cases, the property is distributed according to the personal laws of the deceased. This process is known as intestate succession.
In India, different religious communities have different laws for intestate succession to outline the process for transferring the property without a will.
Hindu Succession Law
The Hindu Succession Act, 1956, applies to Hindus, Sikhs, Jains, and Buddhists.
According to this law:
1. The property first goes to Class I heirs, such as the wife, son, daughter, and mother.
2. If there are no Class I heirs, then Class II heirs, like father, brother, and sister inherit the property.
3. If there are no Class I or II heirs, the property goes to distant relatives or the government.
After the 2005 amendment, daughters have equal rights in ancestral property as sons. This law applies to both self-acquired and inherited properties.
Muslim Succession Law
Muslim succession is governed by personal laws based on the Quran and Sharia. Muslims do not have a uniform civil law like Hindus. The property is divided among heirs known as sharers and residuaries.
Sharers are close relatives like the spouse, parents, and children. Residuaries are other family members who receive the remaining property.
A Muslim can only give up to one-third of their property through a will. The remaining two-thirds must go to legal heirs according to Islamic law.
Christian Succession Law
For Christians in India, succession is governed by the Indian Succession Act, 1925.
When a Christian person dies without a will:
1. The property is divided between the spouse and children.
2. If there are no children, the property goes to the spouse and other relatives, such as parents and siblings.
This law provides equal rights to both sons and daughters.
Parsi Succession Law
Parsis also follow the Indian Succession Act, 1925, but with a few changes. The rules for distributing property are slightly different from those of Christians.
If a Parsi dies without a will, the property is divided among the widow or widower, children, and parents. If there are no close relatives, then the property goes to distant relatives based on a fixed legal order.
Importance of Succession Laws
Succession laws are important for several reasons:
• They provide a clear structure for dividing property.
• They prevent family disputes after the death of a person.
• They protect the legal rights of women, children, and elderly people.
• They ensure that the property is transferred legally and safely.
Legal Documents Required for Succession
If someone dies, their heirs may need to obtain certain legal documents to claim the property. These include:
• Legal Heir Certificate: This document proves who the legal heirs of the deceased are.
• Succession Certificate: This is required to claim movable assets such as bank deposits and insurance.
• Probate: This is the legal process of proving and validating a will in court.
Conclusion
Succession in India depends on whether a person dies with or without a will and also on their religion. Knowing the types of successions and relevant laws helps in managing property transfer smoothly.
It is always a good idea to prepare a will to avoid confusion and conflict in the family. If there is no will, legal heirs should follow the proper legal process based on their personal laws. Understanding succession laws is useful not just for legal professionals but also for every citizen. Being informed can save time, money, and emotional stress.



.webp)




























































































































































































.webp)

































































































.webp)
















































































.webp)